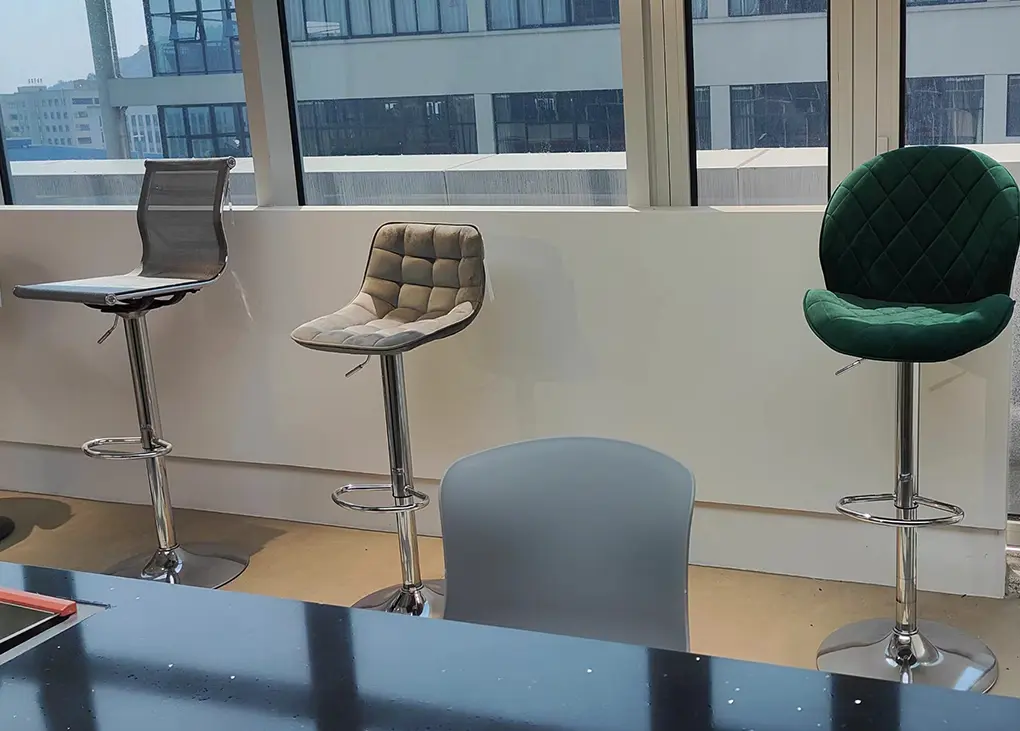
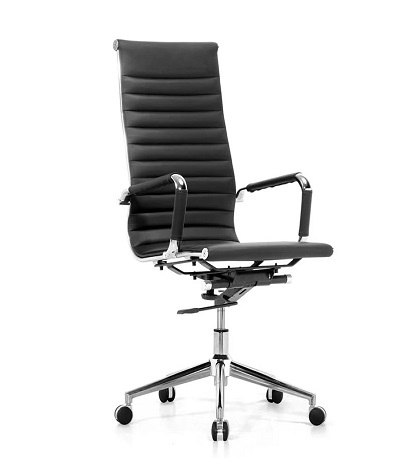
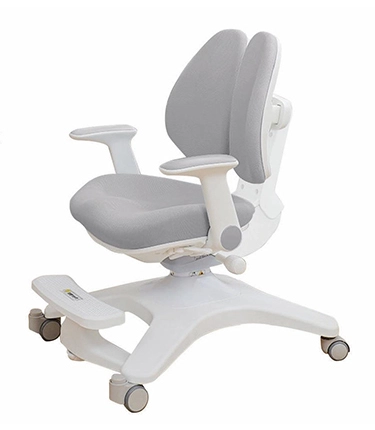
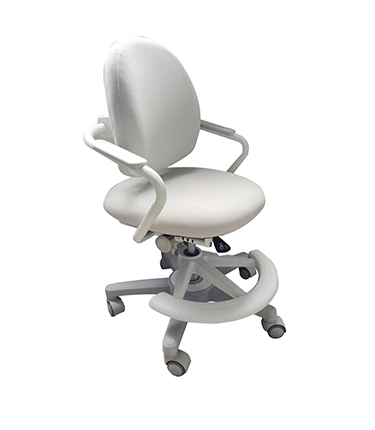
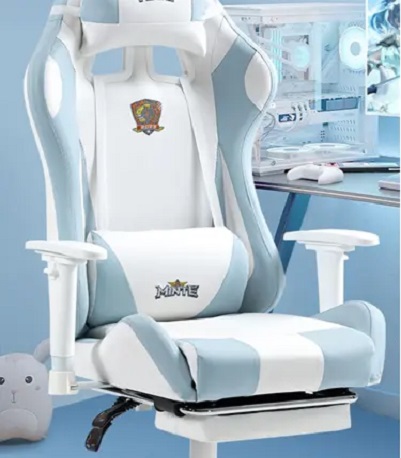
we are dedicated to crafting innovative and sustainable seating solutions that enhance comfort, style, and functionality for every space. Our mission is to inspire creativity and well-being through thoughtfully designed chairs that cater to diverse lifestyles and environments. We prioritize quality craftsmanship, eco-friendly materials, and exceptional customer service, ensuring that every product not only meets but exceeds our customers' expectations. Together, we aim to create a more comfortable and beautiful world, one chair at a time.
Search
English
- XC-60001 Leather Swivel Recliner Chair
- XC-60002 Contemporary Recliner Chair
- XC-60003 Affordable Recliner Chairs
- XC-60004 Modern Recliner Chair
- XC-60005 Luxury Leather Recliner Chairs
- XC-70001 Plastic Dining Chairs
- XC-70002 Modern Dining Chairs
- XC-70003 Traditional Dining Chairs
- XC-70004 High Back Leather Dining Chairs
- XC-70005 Metal Dining Chairs

What are you looking for?